Insulin and Diabetes: Everything You Need to Know

Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. At the core of diabetes management is insulin, a hormone that plays a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels. Understanding how insulin works, its role in diabetes, and how to manage it can significantly improve the quality of life for those living with diabetes. In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about insulin and diabetes, from the basics to advanced tips for managing the condition.
Related: American Diabetes Association – What is Insulin?
What is Insulin?
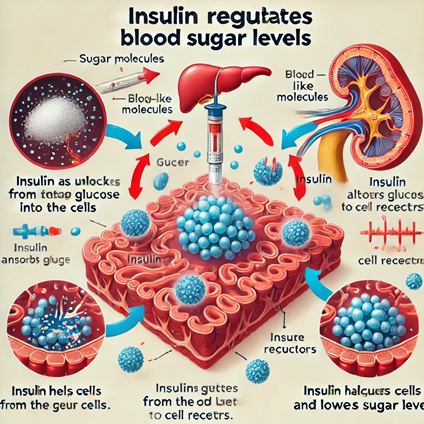
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate the amount of glucose in your blood. After you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. Insulin allows your cells to take in this glucose and use it for energy. Without sufficient insulin, glucose builds up in the blood, leading to high blood sugar levels, which is a hallmark of diabetes.
Types of Diabetes and the Role of Insulin
There are two main types of diabetes, and insulin plays a crucial role in managing both.
- Type 1 Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections or an insulin pump to survive because their bodies no longer produce insulin. - Type 2 Diabetes
In type 2 diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to its effects. While some people with type 2 diabetes can manage the condition through diet, exercise, and medication, others may eventually need insulin therapy.
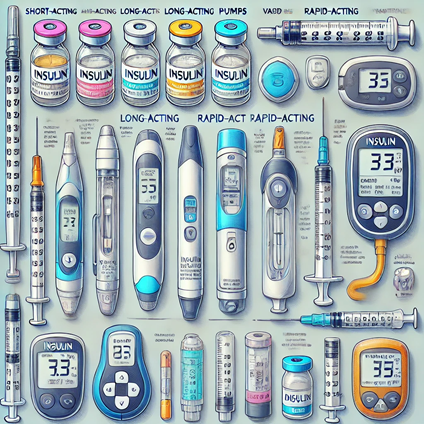
How Insulin Therapy Works
For people who need insulin therapy, there are various options available. The most common types of insulin therapy include:
- Rapid-acting insulin: Taken just before or after meals to control blood sugar spikes.
- Long-acting insulin: Provides a steady level of insulin throughout the day.
- Combination insulin: A mix of rapid-acting and long-acting insulin to meet daily needs.
Insulin can be administered through injections, pens, or insulin pumps. The right method and type of insulin vary depending on individual needs.

The Importance of Blood Sugar Monitoring
If you’re using insulin, regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial. Blood sugar levels can fluctuate based on diet, exercise, stress, and illness, making it essential to track them closely. Tools like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) or traditional glucose meters can help manage these levels effectively.
For resources on how to monitor your blood sugar effectively, check out International Diabetes Federation.

Managing Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells don’t respond properly to insulin, which is common in people with type 2 diabetes. Over time, insulin resistance can lead to higher insulin requirements, making diabetes harder to manage.
Here are some ways to manage insulin resistance:
- Healthy Eating: Focus on a balanced diet with low-glycemic foods, fiber, and lean protein.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity.
- Weight Management: Losing even a small amount of weight can make a big difference in insulin sensitivity.
For more guidance on managing insulin resistance, visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).

Side Effects and Risks of Insulin Therapy
While insulin is lifesaving for people with diabetes, there are potential side effects, including:
- Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar): Can occur if too much insulin is taken or if meals are skipped.
- Weight Gain: Insulin therapy can sometimes lead to weight gain.
- Injection Site Issues: Repeated injections in the same spot can cause skin changes.
It’s essential to work closely with your healthcare team to adjust your insulin dosage and avoid complications. For more detailed insights, visit Mayo Clinic’s page on insulin risks and side effects.

Conclusion
Understanding how insulin works and its role in diabetes management is crucial for anyone living with the condition. By monitoring blood sugar levels, following a healthy lifestyle, and working with your healthcare provider, you can manage your diabetes more effectively.
For more in-depth information about insulin and diabetes, check out the resources at the World Health Organization (WHO).