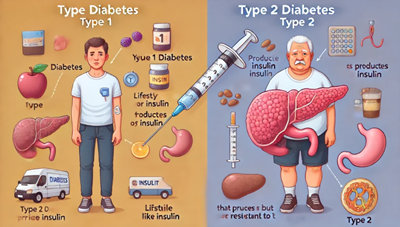
Type 2 Diabetes: Key Causes, Symptoms, and How to Prevent

What is type 2 diabetes ?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body metabolizes glucose, an essential source of energy. Unlike type 1 diabetes, where the pancreas produces little or no insulin, type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production. This can lead to elevated blood glucose levels, which can have serious health consequences.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is often linked to several risk factors, including:
- Genetics: A family history of diabetes increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Overweight: Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, is a significant risk factor.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle contributes to weight gain and insulin resistance.
- Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can increase the risk.
- Age: The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after 45.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes can develop gradually and may include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Extreme fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores or frequent infections
- Areas of darkened skin, usually in the armpits and neck
Many people may not notice symptoms in the early stages, which is why regular check-ups are crucial, especially for those with risk factors.
Complications of Type 2 Diabetes
If left unmanaged, type 2 diabetes can lead to various complications, such as:
- Heart disease and stroke
- Kidney damage (diabetic nephropathy)
- Nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy)
- Eye damage (diabetic retinopathy)
- Foot damage, which may lead to infections and amputations
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
Fortunately, type 2 diabetes can often be prevented or delayed through lifestyle changes:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Aim for a balanced diet and regular exercise to manage your weight.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Be Physically Active: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week.
- Regular Monitoring: If you have risk factors, regular blood sugar monitoring can help catch any changes early.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a serious condition, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and preventive measures can empower individuals to take control of their health. By adopting healthier lifestyle choices, it is possible to reduce the risk of developing diabetes and its complications. Regular check-ups and consultations with healthcare professionals are essential for anyone at risk.